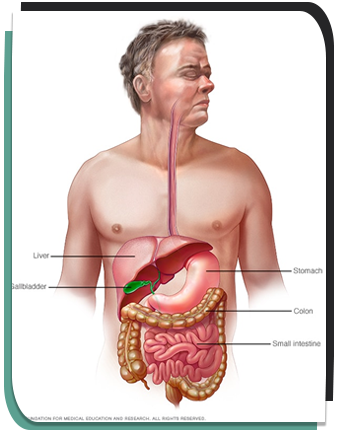
Gastroenterology involves the treatment and diagnosis of digestive system disorders that affect the oesophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, rectum, liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
Most GI studies and procedures are performed on an outpatient basis in Gut Hospital state-of-the-art Endoscopy Suite. The Endoscopy Suite backed by senior gastroenterologist and experienced technician staff offers a welcoming and comfortable environment for patients.
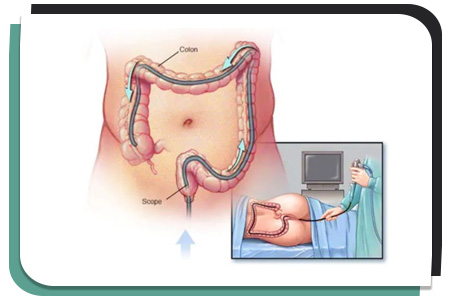
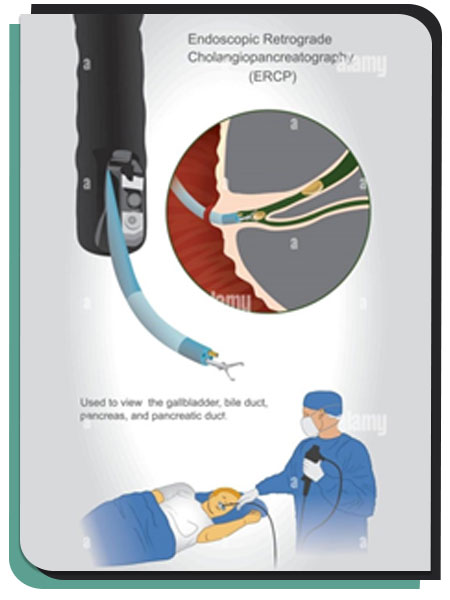
Our endoscopy room is equipped with an armamentarium of latest HD scopes exploring upper GIT (Gastro-scope), Lower GIT (Colono-scope) and Pancreaticobiliary tree (ERCP), Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) enabled with Histogram and Liver probe to analyse vascular details as well stiffness of tissue which is valuable in chronic liver disease as well as in cancers.
All standard protocol of infection control is followed for to patient care & prevent cross infection. High end Endo washer are used for cleaning scopes and UV light cabinets are used for their storage. Full time anesthetist are available to assist in all procedure and provide support to apprehensive patients.